An open-source C++ framework project
The Programmer's Guide
Description
The class place is used for layout managment. Generally, an object of class place is attached to a widget, and it automatically positions and resizes widgets which are the children of the attached widget.
A place divids a widget into fields, and then the children widgets are inserted into a specified field for layouting. The field is a basic concept for place, there are 3 differenct types of field, each type describes how widgets are laied out. These types of field are:
Horizontal: Widgets are laied out horizontally, such as the buttons in a toolbox.
Vertical: Widgets are laied out vertically, such as the items in a menu.
Grid: Widgets are laied out like a grid, such as keys on the keyboard.
Model of
None
Public base classes
None
Typedefs
| field_reference | A reference of a field manipulator which refers to a field object that created by place. Please refer to Note 1 for details of the field manipulator. |
Members
| place() | The construction. |
| place(window wd) | Attaches to a specified widget. |
| ~place() | The destructor |
| void div(const char* divide_text) | Divides the attached widget into fields. Please refer to Note 2 for the syntex of divide-text. |
| field_t& field(const char* name) | Returns a field by the specified name. |
| void collocate() | Layouts the widgets. |
| static unspecified fixed(window wd, unsigned size) | Generates a fixed object to send it to the field. |
| static unspecified percent(window, int per) | Generates a percent object to send it to the field. |
| static unspecified room(window wd, unsigned width, unsigned height) | Generates a room object to send it to the field. |
File
nana/gui/place.hpp
Notes
Note 1:
| The definition of field manipulator: class field_t { public: virtual ~field_t() = 0; virtual field_t& operator<<(nana::gui::window) = 0; virtual field_t& operator<<(unsigned gap) = 0; virtual field_t& operator<<(const implementation-specified-fixed-type&) = 0; virtual field_t& operator<<(const implementation-specified-percent-type&) = 0; virtual field_t& operator<<(const implementation-specified-room-type&) = 0; virtual field_t& fasten(nana::gui::window) = 0; }; |
Note 2:
| The syntex of divide-text. The divide-text is used to divide a widget into fields to position and resize its children widgets. Define a field <> Fields can be nested. <<>> Root field There is an implicit root field. All the fields that defined by divide-text are children of root field. Specify attributes for a field. name: Specify an identifier for a name of field. <id_you_specified> The field is named id_you_specified, and we can refer to it by using place_obj.field("id_you_specified"). vertical: Specify a field that all its children fields are laied out vertical. If it is not specified, its children fields are laied out horizontally defaultly. For example. place plc(fm); plc.div("<abc>"); plc.field("abc")<<btn0<<btn1<<btn2<<btn3; plc.collocate();  If we replace this line plc.div("<abc>"); into plc.div("<vertical abc>"); adn we will get 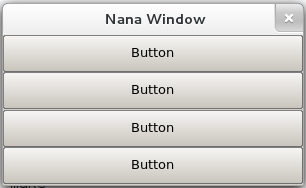 weight: It stands for the width or height of a field. It depends on the type of its owner field's layout. Specify the weight in pixel. <abc><weight=200 def> If the width of form is 1000px, the field abc is 800px and def is 200. <abc><weight=60% def><ghi> If the width of form is 1000px, the field abc is 200px, def is 600px and ghi is 200px. grid [X, Y]: It specify a field that lays its children widgets out as a grid. <grid [3, 2]> The field is divided a 3 X 2 grid. place plc(fm); plc.div("<grid [3, 2] abc>"); plc.field("abc")<<btn0<<btn1<<btn2<<plc.room(btn3, 3, 1); 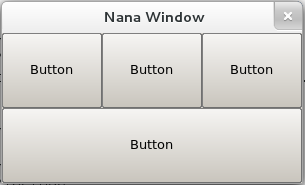 gap: It specify a gap in pixel between widgets for the grid field. <grid [3, 2] gap=5> |
|
Note 3:
| An illustration for the place. Let's create an user interface for validation. The program looks like. 
First of all, we should divide the form into fields. For this result, it may be divided like this 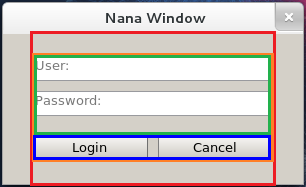
The divide-text of red rectangle should be: <><weight=80% vertical children_fields_of_red_rectangle><> The root field is horizontal defaultly, so these 3 fields are laied out horizontally. The red rectangle in the middle takes 80% spaces, we specify its weight is 80%. As you see, the children of red rectangle are laied out vertically, it should be specified by vertical. The divide-text of orange rectangle. <><weight=70% vertical children_fields_of_orange_rectangle><> The orange rectangle is laied out in the middle about 70% space, it also specified with vertical. The divide-text of green rectangle and blue rectangle. <vertical textboxs><weight=25 buttons> The widgets in green rectangle are laied out vertically, and widgets in blue rectangle are laied out horizontally, so we only specify the vertical for the green rectangle. And the blue rectangle manages buttons and it is horizontal, in other words, the height of blue rectangle is same as buttons', so we specify its weight is 25 pixels. These 2 fields we will refer to and then insert widgets into them, so a name is given for each field. The combination of these divide-texts. <><weight=80% vertical <><weight=70% vertical <vertical textboxs><weight=25 buttons>><>><> Let's start programming. #include <nana/gui/wvl.hpp> #include <nana/gui/place.hpp> #include <nana/gui/widgets/button.hpp> #include <nana/gui/widgets/textbox.hpp> int main() { using namespace nana::gui; //Define widgets form fm; textbox usr(fm), pswd(fm); button login(fm), cancel(fm); usr.tip_string(STR("User:")).multi_lines(false); pswd.tip_string(STR("Password:")).multi_lines(false).mask('*'); login.caption(STR("Login")); cancel.caption(STR("Cancel")); //Define a place for the form. place plc(fm); //Divide the form into fields plc.div("<><weight=80% vertical<><weight=70% vertical<vertical textboxs><weight=25 buttons>><>><>"); //Insert widgets //The field textboxs is vertical, it automatically adjusts the widgets' top //and height. The usr and pswd are single-line textboxs, and we should specify //them with a fixed height. plc.field("textboxs")<<plc.fixed(usr, 25)<<10<<plc.fixed(pswd, 25); plc.field("buttons")<<login<<10<<cancel; //Finially, the widgets should be collocated. //Do not miss this line, otherwise the widgets are not collocated //until the form is resized. plc.collocate(); fm.show(); exec(); } |
See also
None.
Move to The Nana Programmer's Guide Main Page